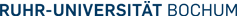Di- and Trifluoromethylations
Cu-catalyzed Trifluoromethylation of Aryl Iodides with Potassium (Trifluoromethyl)trimethylborate
The presence of trifluoromethyl groups in organic compounds has a profound effect on their chemical and physical properties. Trifluoromethyl-substituted compounds often display an improved metabolic stability, a better receptor binding selectivity, increased bioavailability, or stronger dipole moments than non-fluorinated analogs. The development of new methods and reagents to selectively introduce trifluoromethyl groups into organic substrates are thus of constant high interest for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and functional materials. We have introduced potassium (trifluoromethyl)trialkoxyborates as new CF3-reagents for nucleophilic trifluoromethylation reactions. These crystalline, shelf-stable salts are easy to handle and accessible in near quantitative yield from the corresponding trialkoxyborate, Ruppert’s reagent (CF3SiMe3), and potassium fluoride.
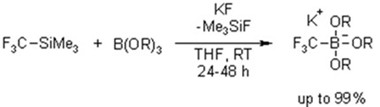
Potassium (trifluoromethyl)trimethoxyborate is successfully employed in copper-catalyzed trifluoromethylations of various aryl iodides. The optimized catalyst system consisting of 20 mol% of copper(I) iodide and 1,10-phenanthroline allows the smooth conversion of various electron-deficient, electron-rich and heterocyclic aryl iodides into their benzotrifluoride derivates in DMSO at 60 °C.
The chemical and physical properties of the CF3-borate salts depend on the alkoxy substituents, and it is thus likely that by varying these side chains, even more effective trifluoromethylating reagents can be developed in the near future. The new reagents may open up new opportunities also for other trifluoromethylation reactions including recently discovered Pd-catalyzed trifluoromethylation of aryl chlorides. New applications of this new class of trifluoromethylating reagents are under investigations.
Key references:
- B. A. Khan, A. E. Buba, L. J. Gooßen, Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 1577-1581: Oxidative Trifluoromethylation of Arylboronates with Shelf-Stable Potassium (Trifluoromethyl)trimethoxyborate. >>DOI
- T. Knauber, F. Arikan, G.-V. Röschenthaler, L. J. Gooßen, Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 2689-2697: Copper-Catalyzed Trifluoromethylation of Aryl Iodides with Potassium (Trifluoromethyl)trimethoxyborate. >>DOI
Sandmeyer-type di- and trifluoromethylations
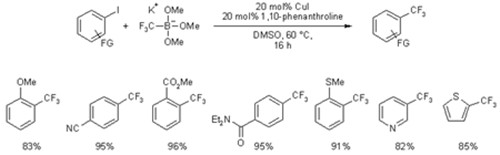
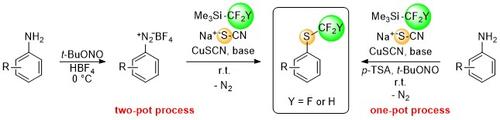
Sandmeyer-type di- and trifluoromethylation processes have been developed that allow the straightforward conversion of (hetero-)arenediazonium salts into the corresponding di-/trifluoromethyl (hetero-)arenes under mild conditions. The actual di-/trifluoromethylating reagent, a di/trifluoromethyl-copper complex, is formed in situ from copper thiocyanate and the inexpensive, easy-to-use reagent TMS-CF2H/ TMS-CF3. The diazonium salts are either pre-formed or generated in situ from broadly available aromatic amines.
Key references:
- G. Danoun, B. Bayarmagnai, M. F. Grünberg, L. J. Gooßen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7972-7975. >>DOI
- C. Matheis, K. Jouvin, L. J. Gooßen, Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 5984-5987. >>DOI
- B. Bayarmagnai, C. Matheis, E. Risto, L. J. Gooßen, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 2343-2348. >>DOI
- G. Danoun, B. Bayarmagnai, M. F. Grünberg, M.; C. Matheis, E. Risto, L. J. Gooßen, Synthesis 2014, 46, 2283. >>DOI
Di- and Trifluoromethylthiolations
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards the corresponding trifluoromethylthio groups, since these enhance the lipophilicity of drug-like molecules even more than their trifluoromethylated analogs (Hansch constant 1.44 for SCF3 vs. 0.88 for CF3). This property improves the bioavailability of drug molecules due to their more effective transport through lipid membranes.
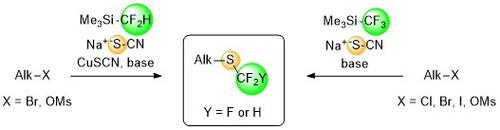
In this context we developed new processes from the same in situ formed di/trifluoromethyl-copper complex that smoothly converts organothiocyanates into valuable di/trifluoromethyl thioethers. This reaction step can be combined with several thiocyanation methods to one-pot protocols, allowing late-stage di-/trifluoromethylthiolations of widely available alkyl halides and arenediazonium salts. These protocols enable the efficient introduction of the pharmaceutically meaningful di- and trifluoromethylthio groups into functionalized drug-like molecules without the need of expensive preformed di-/trifluoromethylthiolating agents.