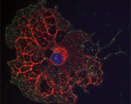
Extracellular matrix molecules are described to be potent mediators of axonal outgrowth and guidance as well as neuronal survival in the central nervous system. We have worked out a model system to investigate the influences of extracellular matrix molecules on cultures of isolated motoneurons of embryonic mice (Conrad et al. 2011). Using this procedure we try to identify the underlying signaltransduction pathways in combination with putative modulators of these cascades. First results showed that matrixmolecules and specific parts of those macromolecules respectively are able to modify axonal outgrowth of the cultured mouse motoneurons and influence their apoptotic properties. To investigate these effects we work with different cell culture systems as well as primary cell cultures and cell lines. Our standard experimental procedure implies immunohistochemistry using embryonic and postnatal mouse cryosections and in addition immunocytochemical staining of cultured cells. Biochemical methods were used to identify the signaltransduction pathways leading to the change of behavior of the cells cultured on the different substrates.