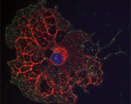
Function of the LRP1 in the radial glia compartment of the mouse brain
LRP1 (Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor-related Protein-1) is a member of the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor family and is expressed in various tissues, including liver, adipose tissue, lungs, blood vessels and the brain. In the central nervous system (CNS) LRP1 is highly expressed in brain endothelial cells, vascular smooth muscle cells, pericytes, the choroid plexus, astrocytes, microglia and neurons.
LRP1 has been shown to be responsible for proper signal transduction, neuronal outgrowth as well as cholesterol transport and metabolism – processes crucial for proper synapse formation. LRP1 interactions with amyloid precursor protein (APP), a2- Macroglobulin (a2- M) and apolipoprotein E (ApoE) – proteins known for their importance in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis – make LRP1 the target of intense research in the field of neurodegenerative diseases.
As the complete knock-out of LRP1 is lethal for mouse embryos (Herz et al., 1992) it is hard to study the function of LRP1 in vivo. Although several LRP1 conditional knock-out and knock-in models are also available, they mostly focus on the role of LRP1 in the adult CNS – the function of LRP1 in brain development and embryogenesis still remains elusive. A recent publication from our lab shows that LRP1 is a novel carrier protein for Lewis-X (LeX) glycans, expressed by radial glia (neural stem precursor cells; NSPCs) in the developing and adult CNS, and is important for neural stem cell differentiation: NSPCs with a LRP1 conditional knock-out in vitro generate fewer oligodendrocytes (Hennen et al., 2013). My PhD project focuses on unraveling the function of LRP1 during mouse brain development by using a telencephalon specific conditional knock-out mouse model.
[1] Hennen, E., Safina, D., Haussmann, U., Wörsdörfer, P., Edenhofer, F., Poetsch, A., and Faissner, A. (2013).
[2] A LewisX glycoprotein screen identifies the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP1) as a modulator of oligodendrogenesis in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 16538-16545.
[3] Herz, J., Clouthier, D.E., and Hammer, R.E. (1992). LDL receptor-related protein internalizes and degrades uPA-PAI-1 complexes and is essential for embryo implantation. Cell 71, 411–421. (Author’s correction, Cell (1993) 73, 428).
Short academic CV:
- 01. 10. 2014 PhD at the Department of Cell Morphology and Molecular Neurobiology, Ruhr-University Bochum
- 2006-2011 Master studies in the field of Biology at the Jagiellonian University, Cracow, Poland
Applied methods:
- Neural stem cell and astrocytic cultures
- Immunocytochemistry
- Immunohistochemistry
- DNA and RNA isolation
- cDNA synthesis
- PCR
- RT-PCR
- Isolation of proteins
- Western Blot
- Axiophot
- LSM
- Digital video microscopy