miRNA expression in PDAC, chronic pankreatitis and cell lines
Szafranska AE, Davison TS, John J, Cannon T, Sipos B, Maghnouj A, Labourier E, Hahn SA. ![]() MicroRNA expression alterations are linked to tumorigenesis and non-neoplastic processes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 2007 Jun 28;26(30):4442-52. Epub 2007 Jan 22. PMID: 17237814
MicroRNA expression alterations are linked to tumorigenesis and non-neoplastic processes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 2007 Jun 28;26(30):4442-52. Epub 2007 Jan 22. PMID: 17237814
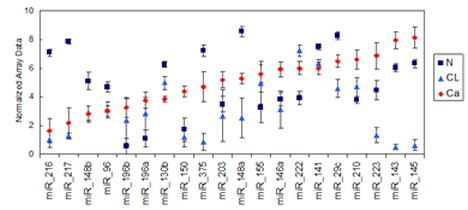
miRNA expression in cell line (CL), normal (N) and PDAC (Ca) samples for the top 20 miRNAs most differentially expressed in pancreatic tissues. The graph shows mean normalized expression values and standard deviations in the 3 sample types for the 20 miRNAs identified in Figure 3C with a │Dh│>1.6 and p-value<0.0001 between at least 2 out of the 3 primary tissue types.
INTRODUCTION
Recently, microRNAs (miRNAs), a novel class of 18-23 nt long non-coding RNAs, have gained attention as another family of molecules involved in cancer development. Upon binding to their target RNAs, miRNAs cause postranscriptional gene silencing by either cleaving the target mRNA or by inhibiting the translation process. Misregulation of miRNAs has been demonstrated in a number of hematological as well as solid tumor entities and are likely contributing to tumor development and progression. Due to their high stability even in poorly preserved specimen, miRNAs are expected to be robust clinical analytes, valuable for clinical research and biomarker discovery. By virtue of their apparent role in tumorigenesis, miRNAs may not only be potential targets for new prognostic and diagnostic strategies but also have therapeutic potential. A recent publication has shown that anti-miRNA oligonucleotides conjugated with cholesterol, also called antagomirs, are able to inhibit miRNA function in vivo in a mouse model system, indicating that therapeutic adjustment of miRNA over-expression in a given cancer type may become feasible. Similarly, it should be possible to correct miRNAs down regulated in tumors using miRNA expression strategies such as viral delivery systems.
CURRENT MIRNA RESEARCH ACTIVITIES AT OUR GROUP
Three studies (see below), including a study from our group, have analyzed miRNA expression in pancreatic cancer. Building on these results, our group aims at characterizing and validating miRNAs as novel therapeutic targets for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) in relevant preclinical models. MiRNA suppression as therapeutic option is hampered by stability, specificity, bioavailability and cellular uptake of miRNA knock-down compounds. Thus, apart from characterizing and validating miRNAs in PDAC, we also focus in collaboration with Prof. Dr. N. Metzler-Nolte, Bioorganic Chemistry ![]() , Ruhr-University Bochum on a novel approach to potentially overcome some of the afore mentioned problems. We aim at combining peptide nucleic acid (PNA) technology with its known superior stability and excellent sequence discrimination with tumor cell type specific uptake by coupling antisense PNA molecules to target miRNAs with receptor specific peptides.
, Ruhr-University Bochum on a novel approach to potentially overcome some of the afore mentioned problems. We aim at combining peptide nucleic acid (PNA) technology with its known superior stability and excellent sequence discrimination with tumor cell type specific uptake by coupling antisense PNA molecules to target miRNAs with receptor specific peptides.
ADDITIONAL REPORTS ON MIRNA EXPRESSION IN PDAC
Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F, Volinia S, Alder H, Hagan JP, Liu CG, Bhatt D, Taccioli C, Croce CM (2007) MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. Jama 297: 1901-1908.
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J, Nuovo GJ, Lerner MR, Frankel WL, Morgan DL, Postier RG, Brackett DJ, Schmittgen TD (2006) Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 120:1046-1054.
DOWNLOADS
Normalized Array Data for 6 Individual Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines (IMIMPC2, PT45, PL45, PanTu1, PaCa44) and 3 Tissue Types (Pancreatic Cancers (Ca), Chronic Pancreatitis (Ch), and Normal Pancreas (N)) ![]() download
download
Normalized Array Data for 19 Individual Tissue Samples: 8 Pancreatic Cancers (Ca), 6 Chronic Pancreatitis (Ch), and 5 Normal Pancreas (N) ![]() download
download